The Reinforcing Effect of Hydrophobic Fumed Silica in Organosilicon Foaming Materials
Organosilicon foams are renowned for their low density, exceptional thermal insulation capabilities, and impressive mechanical strength, making them highly desirable for various applications in industries such as ealing materials, cushioning materials, and other fields.
These fields have higher requirements for material strength. If the strength does not meet the standards, it will affect properties of shock absorption, compression resistance, and resilience.
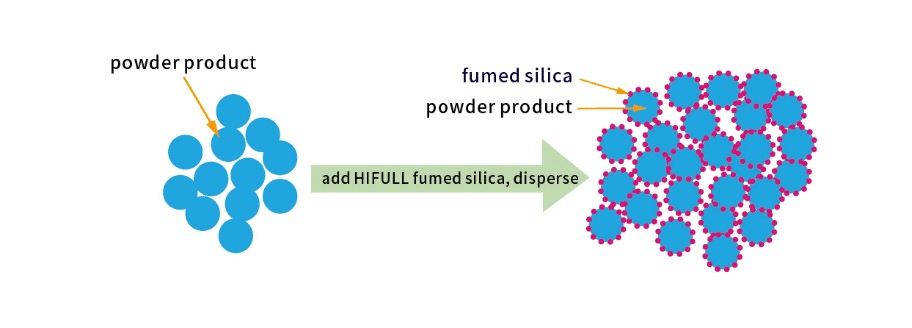
Among the various reinforcing fillers available, hydrophobic fumed silica has emerged as a particularly promising candidate for organosilicon foaming materials. The use of hydrophobic fumed silica as a reinforcing filler offers several advantages, including improved interfacial adhesion, enhanced dispersion within the foam matrix, and the potential to mitigate moisture-related issues in the foam structure.
Properties of Hydrophobic Fumed Silica
Hydrophobic fumed silica exhibits several desirable properties that make it an effective reinforcing filler in organosilicon foaming materials.
Firstly, its high surface area enables strong interfacial interactions with the polymer matrix, leading to improved mechanical properties.
Secondly, the nano-sized silica particles act as physical barriers, impeding crack propagation and enhancing the material’s resistance to deformation.
Furthermore, the hydrophobic nature of fumed silica minimizes moisture absorption, which can weaken the foam structure and degrade its performance over time. This moisture resistance is particularly advantageous in applications exposed to humid or wet environments.
Experimental Methods
Let’s check out by an experiment
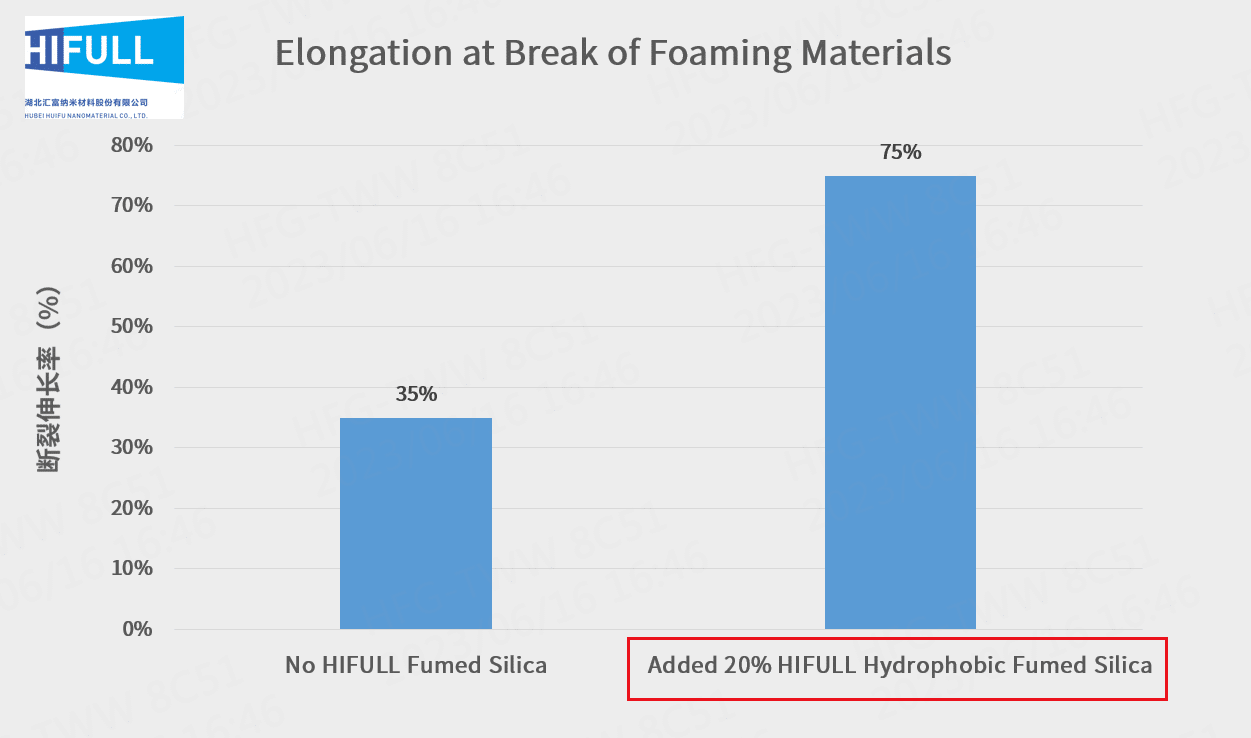
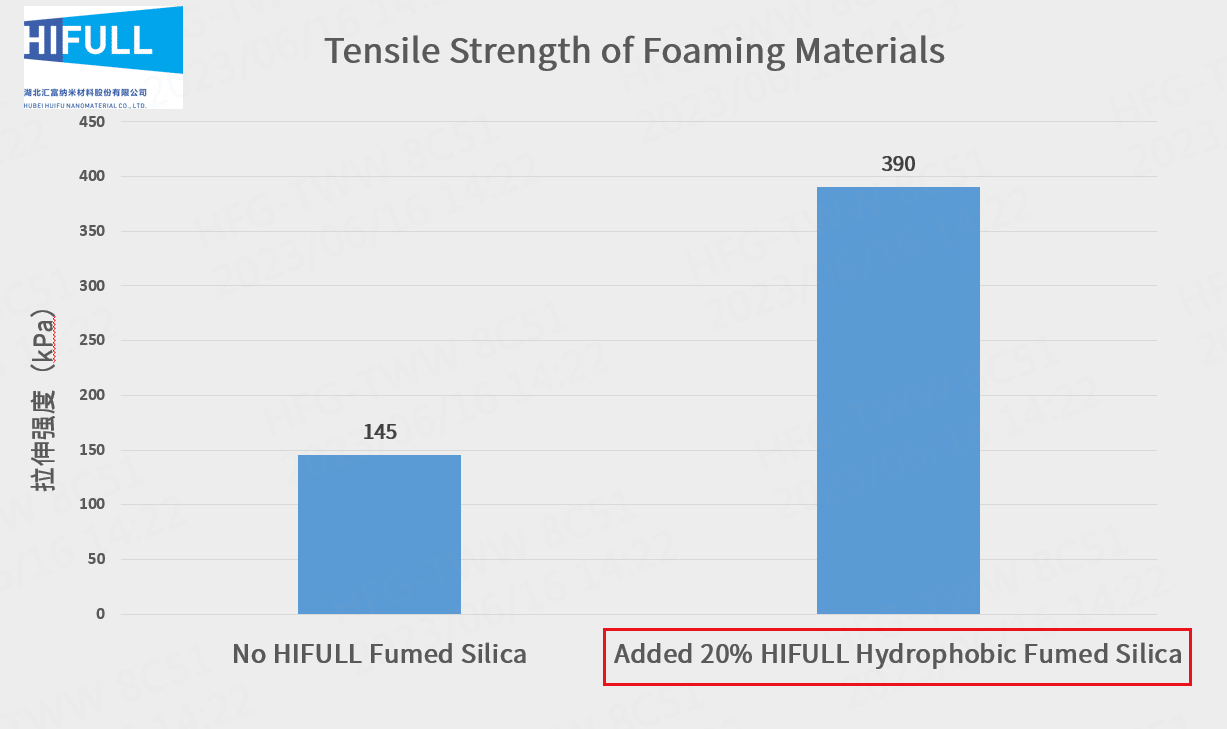
The data shows that the sample added fumed silica has higher tensile strength and elongation at break compared to the one not.
It shows fumed silica can enhance the tensile and tear strength of organosilicone foaming materials as reinforcing agent.